Programme
The IB Diploma Programme
How is the IB Diploma Programme structured?


PreIB
PreIB is a one-year preparatory course for Danish and foreign students who have not completed 11 years of school. In some ways, PreIB is equivalent to the Danish 1.g (STX).
What is PreIB?
Læs mereThe IB Learner Profile
As an IB student (IB1 & IB2), you complete courses from six different subject groups, ensuring a depth and breadth of knowledge, skills and understanding. By engaging with a range of subjects, you will experience a comprehensive education which encourages you to link your learning to ways of applying what you have learned.
This development is supported by three core components:
- Theory of Knowledge (ToK)
- Extended Essay (EE)
- Creativity, Action & Service (CAS)
Throughout the 2-year course, you will sit exams which are externally provided by the International Baccalaureate Organisation (IBO) and marked by a worldwide network of examiners.
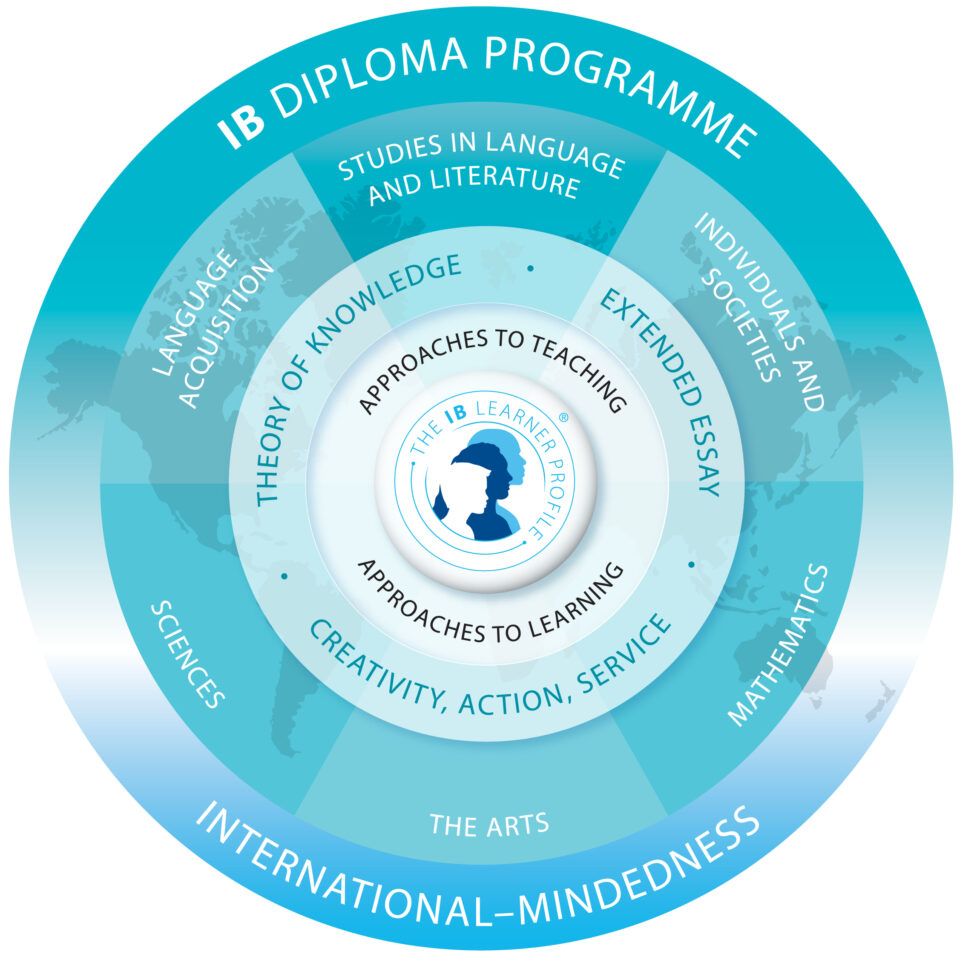
IB subjects (IB1 & IB2)
As an IB student, you complete courses from six different subject groups, ensuring a depth and breadth of knowledge, skills and understanding within languages, matematics, science, social studies and the arts.
The IB Diploma Programme
The IB Diploma Course is divided into six subject groups as illustrated in the IB Diploma curriculum framework:
The following requirements are obligatory to all IB students
The following requirements are obligatory to all IB students
Extended Essay (EE): an independent, self-directed piece of research, culminating in a 4,000-word paper in a subject chosen by the student. At Hasseris Gymnasium & IB World School the process of writing the EE is initiated by the middle of IB1, and the essay is handed in during the autumn of IB2, but already in PreIB students are introduced to the academic method applied when working with the PreIB Historial Investigation. Throughout the EE process the student will receive advice and guidance from a supervisor, the EE coordinator and the librarian.
Theory of Knowledge (ToK): a central requirement to the educational philosophy of the Diploma Programme focusing on critical reflections on diverse ways of knowing, on areas of knowledge and the role and nature of knowledge in the students’ own culture, in the cultures of others and in the wider world. In addition, it prompts students to be aware of themselves as thinkers, encouraging them to become more acquainted with the complexity of knowledge and recognize the need to act responsibly in an increasingly interconnected but uncertain world.
Creativity, Activity and Service (CAS): the extra-curricular activities all IB students must carry out outside school hours.
These requirements represent the core of the IB Diploma Programme and must be passed to obtain the IB Diploma Exam

CAS
As part of their youth education the students must complete a voluntary extracurricular program called CAS (short for Creativity, Activity, Service). The main point of CAS is to teach the students that learning and personal growth should not only take place at school, but must also happen in the community around them.
What is CAS?
Læs mereThe study skills you acquire through IB, especially how to work independently, how to handle many deadlines and work under pressure, have been of great benefit to me as I have begun to study at university level.
